Minimum Wages Rules in Haryana
In Haryana, the government sets Minimum Wages Rules in Haryana to ensure fair compensation for workers across various skill levels—unskilled, semi-skilled, skilled, and highly skilled. These wages are revised twice a year, in January and July, considering inflation and the cost of living. The minimum wage serves as a baseline salary for all workers, safeguarding their living standards while ensuring financial stability. The Haryana State Government determines the wage structure for different categories, including clerical and other occupational roles. Employers are legally required to pay at least the prescribed minimum wage, which includes basic salary and allowances, and compensate overtime at the applicable rate. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal action, or other penalties, and employees have the right to file grievances with the Labour Department in case of wage violations. To uphold these standards, the government conducts regular inspections, ensuring that workers receive their entitled wages and benefits.
Complete Guide to Minimum Wage in Haryana!
Minimum Wage Regulations in Haryana: Simple Guide
The Minimum Wages Rules in Haryana ensure that workers receive fair pay based on their skill level, whether they are unskilled, semi-skilled, skilled, or highly skilled. Moreover, the government updates wages twice a year, in January and July, to keep up with inflation and the cost of living. These wages apply to various jobs, including agriculture, construction, manufacturing, and clerical work. Additionally, employers must pay at least the fixed minimum wage, which includes basic salary and dearness allowance (DA). Furthermore, if an employee works for more than 9 hours a day or 48 hours a week, they must be paid overtime at double the regular rate. To promote transparency, businesses are required to keep proper wage records and display the latest minimum wage notices at workplaces.
In addition, the Labour Department of Haryana keeps a check on employers through regular inspections to ensure they follow the rules. If an employer fails to comply, they can face fines, legal action, or even imprisonment. Importantly, workers who are underpaid have the right to file a complaint with the Labour Department. Besides this, employers must follow legal deduction rules and provide additional benefits like paid leave and bonuses. Since the Minimum Wages Act, 1948, has been in force, Haryana has been regularly updating wages to ensure workers receive fair earnings based on current economic conditions. Overall, these rules help protect workers from unfair wages while ensuring that businesses stay legally compliant.
Minimum Wage Structure & Worker Categories in Haryana
Minimum wage system ensures that workers get fair pay based on their skills and job type. The government updates these wages twice a year in January and July, considering factors like inflation, living costs, and industry standards. Minimum wages include basic salary and dearness allowance (DA) to help workers manage their expenses. These wages apply across different sectors like agriculture, construction, factories, and office jobs, ensuring fair pay for all.
Types of Workers in Haryana
- Unskilled Workers
Jobs that don’t need special training, like helpers, laborers, loaders, and housekeeping staff. - Semi-Skilled Workers
Workers with some experience or basic training, such as drivers, machine operators, and junior technicians. - Skilled Workers
People with proper training and expertise, including welders, carpenters, electricians, and experienced machine operators. - Highly Skilled Workers
Professionals with specialized knowledge, like engineers, toolmakers, and high-tech industry workers.
Employers must pay at least the fixed minimum wage for each category. If they don’t, they can face fines or legal action, and workers have the right to complain to the Labour Department. The government regularly checks workplaces to make sure businesses follow these rules. These wage laws help protect workers from being underpaid and ensure that businesses operate legally while supporting their employees.
The Labor Department’s Role in Fair Wages in Haryana
Haryana Labor Department works to make sure workers get paid fairly and on time. It enforces wage laws, keeps an eye on employers, and steps in when workers face unfair treatment. Here’s how it plays a crucial role in protecting wages and workers’ rights.
What Does the Labor Department Do?
- Sets and Updates Minimum Wages
- The department decides the minimum wages for different jobs and industries.
- It reviews wages from time to time to match the cost of living.
- Checks If Employers Are Following Wage Laws
- Labor officers visit workplaces to make sure workers are getting paid what they should.
- If companies break the rules, they face fines and legal action.
- Resolves Wage Disputes
- If a worker isn’t paid on time or gets less than they should, they can complain to the department.
- Officials help resolve issues and ensure workers receive their rightful earnings.
- Ensures Timely Salary Payments
- Under wage laws, salaries must be paid on time without unfair deductions.
- If an employer delays payments, action is taken against them.
- Protects Contract and Daily Wage Workers
- Many workers are on contracts or work in informal jobs.
- The department ensures they too, get fair wages and benefits.
- Spreads Awareness About Worker Rights
- Many workers don’t know what wages they are entitled to.
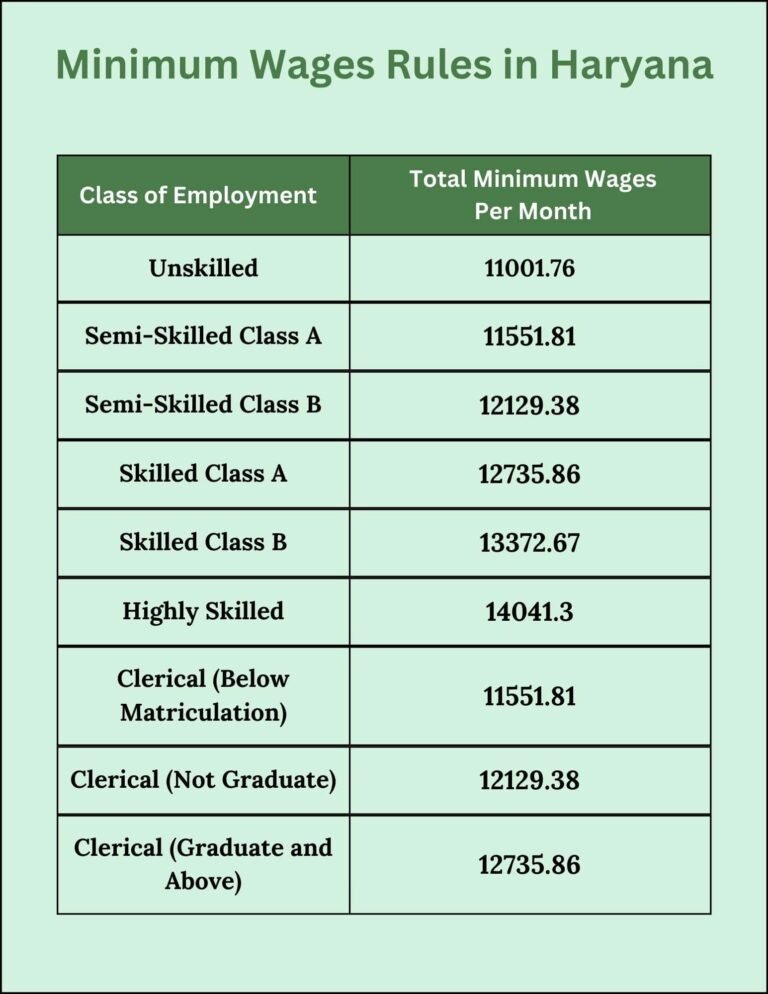
What Are the Latest Monthly Minimum Wages in Haryana?
The Minimum Wages Rules in Haryana are determined based on the worker’s skill level, qualifications, and experience. Below is a table showing the latest wage rates applicable to different worker categories, ensuring fair compensation and compliance with government regulations.
Class of Employment | Total Minimum Wages Per Month (₹) |
Unskilled | 11001.76 |
Semi-Skilled Class A | 11551.81 |
Semi-Skilled Class B | 12129.38 |
Skilled Class A | 12735.86 |
Skilled Class B | 13372.67 |
Highly Skilled | 14041.3 |
Clerical (Below Matriculation) | 11551.81 |
Clerical (Matriculation, Not Graduate) | 12129.38 |
Clerical (Graduate and Above) | 12735.86 |
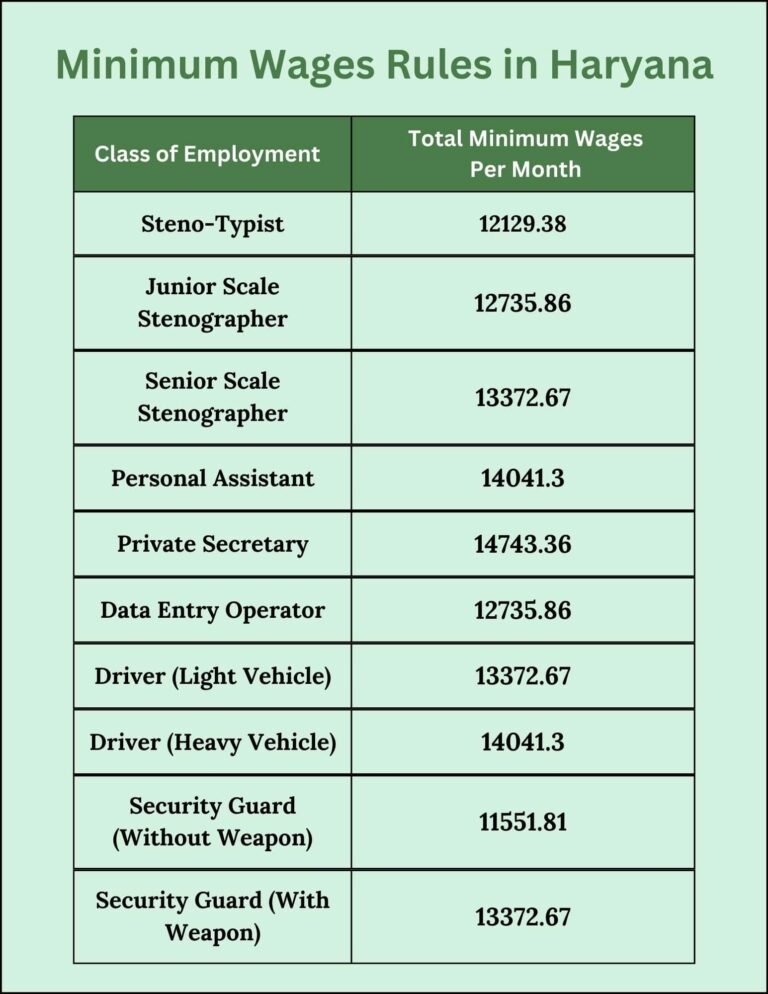
Steno-Typist | 12129.38 |
Junior Scale Stenographer | 12735.86 |
Senior Scale Stenographer | 13372.67 |
Personal Assistant | 14041.3 |
Private Secretary | 14743.36 |
Data Entry Operator | 12735.86 |
Driver (Light Vehicle) | 13372.67 |
Driver (Heavy Vehicle) | 14041.3 |
Security Guard (Without Weapon) | 11551.81 |
Security Guard (With Weapon) | 13372.67 |
Minimum Wages Rates and Regulations for Security Agencies and Guards
Security agencies in Haryana must follow these rules to ensure fair pay and good working conditions for security guards:
- Pay as per Government Rates
Security guards must get the minimum wages set by the government, which are updated twice a year (January & July). - Wage Rates
Unarmed security guards should be paid at least ₹11,551.81 per month, while armed guards must get ₹13,372.67 per month, including basic pay and allowances. - Overtime Payment
If a guard works more than 8 hours a day or 48 hours a week, they must be paid overtime at twice the normal rate. - Salary Payment on Time
Agencies must pay wages by the 7th of every month without any delay. - PF and ESI Benefits
Security guards must get Provident Fund (PF) and Employee State Insurance (ESI) benefits, if eligible. - Keep Proper Records
Agencies must maintain attendance, salary slips, and payment records to ensure transparency and avoid fines. - Leave and Holidays
Guards are entitled to paid leaves, national holidays, and other benefits as per labor laws. - No Unfair Deductions
Agencies cannot deduct wages except for PF, ESI, or legally allowed reasons. - Government Inspections
The Labour Department regularly checks and audits security agencies to ensure they follow wage rules. - Penalties for Violations
If an agency fails to follow wage rules, they may face fines, suspension of their license, or legal action.
Security agencies must follow these rules to ensure their guards get fair pay and benefits, and to avoid legal trouble.
Haryana’s Latest Law Updates and Reforms
- Labor Law Reforms
- Higher Minimum Wages for different worker categories.
- Stricter worker protection against unfair wages and labor exploitation.
- Simplified labor law compliance for businesses.
- Business and Industry Reforms
- Faster business approvals with an online system.
- Financial support for MSMEs to boost small businesses.
- Land law changes to help industries grow while ensuring fair compensation.
- Urban and Rural Development
- Affordable housing schemes for low-income groups.
- Smart city improvements for better sanitation and traffic management.
- Stronger property laws to prevent fraud and disputes.
- Education and Welfare Reforms
- Job training programs to improve youth employment.
- Stronger laws to protect women and children.
Ensured reservations for economically weaker sections in jobs and education.
How to Recover Unpaid Wages: Legal Steps Explained
If your employer hasn’t paid your salary, don’t panic. First and foremost, check your salary slips, appointment letter, and bank records to confirm how much is pending. Next, try talking to your employer or HR—they might resolve the issue without any trouble. However, if that doesn’t work, send a written notice asking for your payment with a clear deadline.
If the employer still ignores you, you can file a complaint with the Labor Commissioner’s Office, which handles salary disputes. Furthermore, if needed, you can take legal action under the Payment of Wages Act, 1936, or file a case in court. In some cases, the court may even order your employer to pay extra for the delay. Alternatively, mediation or arbitration can help settle things quickly. By following these steps, you can ensure you get the money you rightfully earned.
Conclusion: The Impact of Minimum Wage Laws in Haryana
Minimum Wages Rules in Haryana laws help ensure that workers get fair pay for their hard work. By establishing wage rates based on skill and industry, these laws protect employees from being underpaid and help them maintain a decent standard of living. Moreover, regular updates in wages help workers cope with rising costs and inflation.
Despite these regulations, some employers still try to avoid paying the minimum wage, and many workers don’t know their rights. To address this issue, the government needs to ensure stricter enforcement and spread awareness among workers. Ultimately, these wage laws not only support employees but also create a fair work environment that benefits businesses and the economy as a whole.